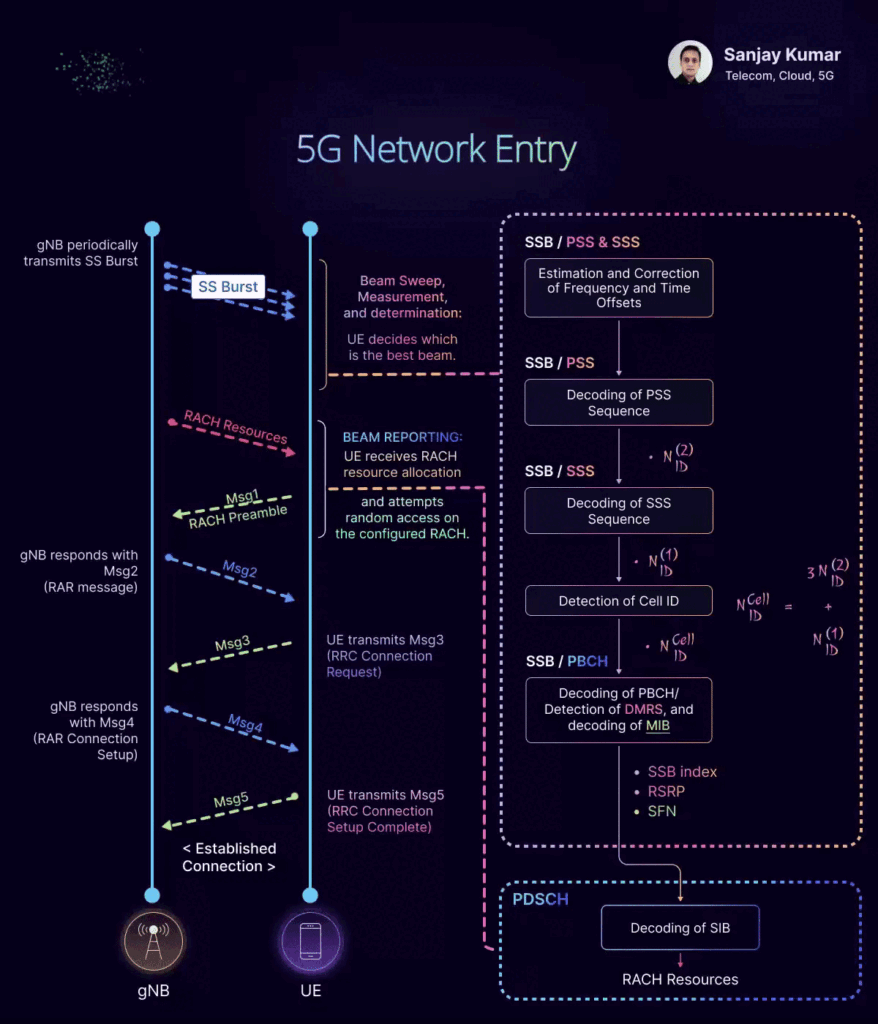
𝟓𝐆 𝐍𝐞𝐭𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐤 𝐄𝐧𝐭𝐫𝐲 𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐞𝐝𝐮𝐫𝐞
5G Network Entry refers to the process and procedures involved in connecting a user device to a 5G network. This involves several steps and interactions between the device (User Equipment, UE) and the network infrastructure (including the gNB, which is the 5G base station, and the core network).
𝑯𝒆𝒓𝒆’𝒔 𝒂 𝒉𝒊𝒈𝒉-𝒍𝒆𝒗𝒆𝒍 𝒐𝒗𝒆𝒓𝒗𝒊𝒆𝒘 𝒐𝒇 𝒕𝒉𝒆 5𝑮 𝒏𝒆𝒕𝒘𝒐𝒓𝒌 𝒆𝒏𝒕𝒓𝒚 𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒄𝒆𝒔𝒔:
𝑺𝒕𝒆𝒑 1 -𝑪𝒆𝒍𝒍 𝑺𝒆𝒂𝒓𝒄𝒉 𝒂𝒏𝒅 𝑺𝒆𝒍𝒆𝒄𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏:
The UE searches for available cells and selects the best one based on signal strength and quality. This involves synchronization with the cell’s primary and secondary synchronization signals (PSS and SSS).
𝑺𝒕𝒆𝒑 2 – 𝑺𝒚𝒔𝒕𝒆𝒎 𝑰𝒏𝒇𝒐𝒓𝒎𝒂𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏 𝑨𝒄𝒒𝒖𝒊𝒔𝒊𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏:
The UE decodes the Master Information Block (MIB) and System Information Blocks (SIBs) to get essential information about the network, such as cell identity, configuration parameters, and access restrictions.
𝑺𝒕𝒆𝒑 3 – 𝑹𝒂𝒏𝒅𝒐𝒎 𝑨𝒄𝒄𝒆𝒔𝒔 𝑷𝒓𝒐𝒄𝒆𝒅𝒖𝒓𝒆 (𝑹𝑨𝑪𝑯):
The UE initiates a Random Access Channel (RACH) procedure to request access to the network. This involves sending a RACH preamble to the gNB.
The gNB responds with a Random Access Response (RAR), which includes timing advance information and an uplink grant for the UE to send its initial message.
𝑺𝒕𝒆𝒑 4- 𝑪𝒐𝒏𝒏𝒆𝒄𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏 𝑬𝒔𝒕𝒂𝒃𝒍𝒊𝒔𝒉𝒎𝒆𝒏𝒕:
RRC Connection Setup: The UE sends an RRC Connection Request message to the gNB, which responds with an RRC Connection Setup message. The UE then sends an RRC Connection Setup Complete message to confirm the connection.
NAS Signaling: The UE and the core network exchange Non-Access Stratum (NAS) messages for authentication and security procedures. This includes the Authentication Request/Response and Security Mode Command/Complete messages.
𝑺𝒕𝒆𝒑 4 – 𝑨𝒖𝒕𝒉𝒆𝒏𝒕𝒊𝒄𝒂𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏 𝒂𝒏𝒅 𝑺𝒆𝒄𝒖𝒓𝒊𝒕𝒚
𝑺𝒕𝒆𝒑 5 – 𝑰𝒏𝒊𝒕𝒊𝒂𝒍 𝑹𝒆𝒈𝒊𝒔𝒕𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏
𝑺𝒕𝒆𝒑 6 – 𝑷𝑫𝑼 𝑺𝒆𝒔𝒔𝒊𝒐𝒏 𝑺𝒆𝒕𝒖𝒑
Steps 4, 5 &6 will be discussed in the next post.
For more content like this, Please follow Sanjay Kumar ↗️ and TelcoLearn
#5g #5gnr #5gcore #5gtraining #telcolearn
